1. Master Bus Monitoring
Setup: Insert analyzer as the last plugin on your master channel.
Purpose: Continuously monitor your entire mix's frequency balance as you work. Catch problems before they accumulate.
Workflow: Keep analyzer visible in second monitor or floating window. Glance at it while mixing to ensure balanced spectrum.
Pro Tip: Use peak hold mode to capture transients and temporary frequency spikes during dynamic sections.
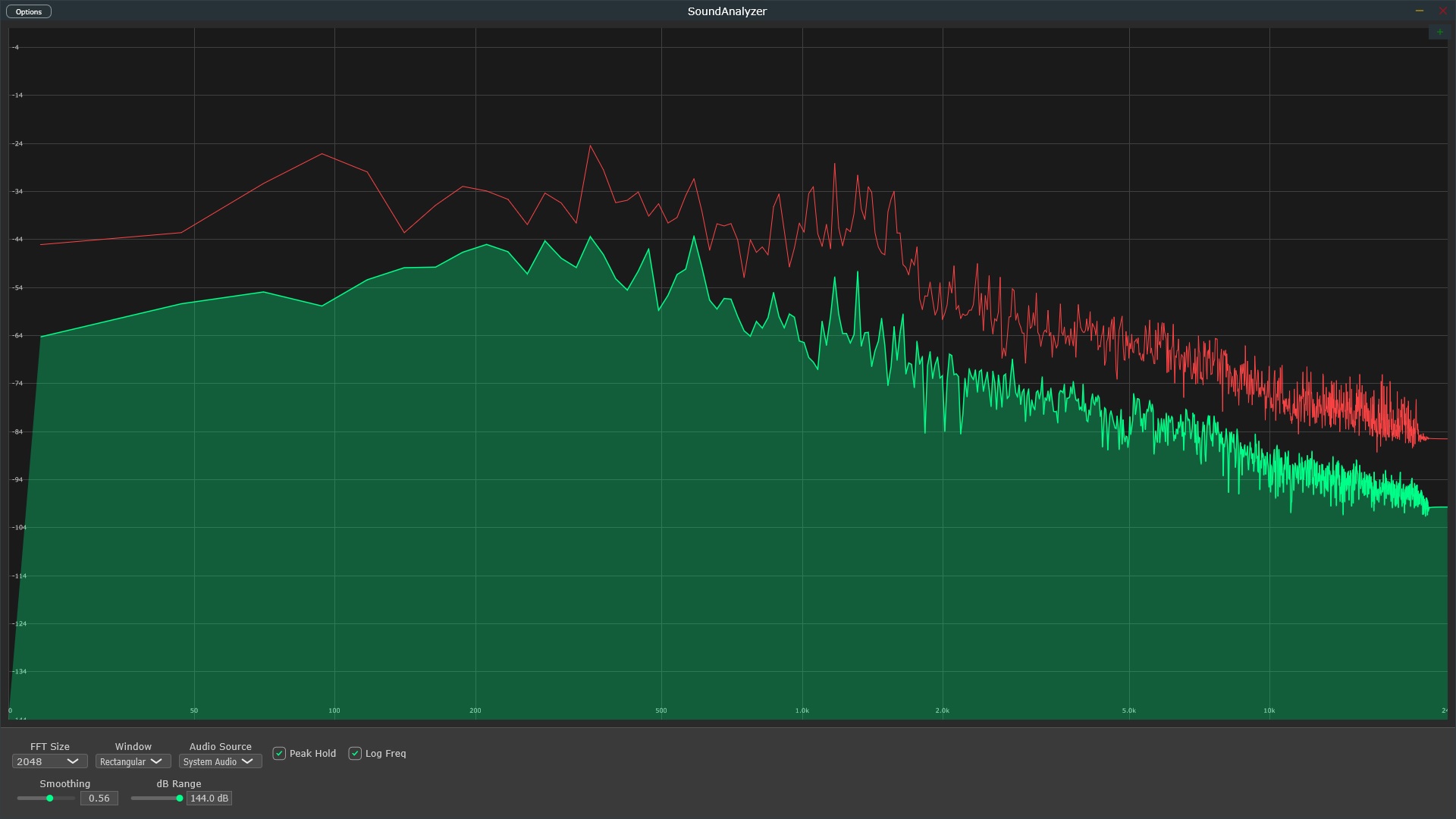
2. Reference Track Comparison
Method: Import reference track into your DAW. Route it and your mix through separate analyzer instances.
Analysis: Compare frequency balance, low-end energy, high-frequency extension, and midrange density between tracks.
Critical Rule: Match similar song sections (verse to verse, chorus to chorus). Don't compare static snapshots.
Action: Make subtle EQ adjustments to bring your mix's balance closer to the reference without exact copying.
3. Frequency Conflict Resolution
Problem Detection: When two instruments sound muddy together, load analyzer on each track's channel.
Visual Analysis: Solo each track and note where their dominant frequencies overlap (usually 200-500 Hz for muddiness).
Solution: Use subtractive EQ - cut the less important element at the conflicting frequency, boost the more important one if needed.
Result: Each element occupies its own sonic space with clear separation and definition.
4. EQ Decision Verification
Before/After: Insert analyzer before and after EQ plugin to visualize exactly what your EQ is doing.
Learning Tool: Train your ears by making EQ changes with eyes closed, then verify with analyzer. Develop better frequency recognition.
Precision: Confirm you're cutting/boosting the intended frequencies. Catch mistakes like boosting wrong harmonic.
Mastering: Essential for subtle mastering EQ moves where changes are harder to hear but visible on spectrum.
5. Low-End Management
Bass Analysis: Insert analyzer on bass and kick drum channels to see where each instrument's fundamental frequency lives.
Conflict Resolution: If both peak at same frequency (e.g., 80 Hz), notch one and boost the other to create space.
Sub-Bass Check: Verify nothing below 30 Hz except intentional sub-bass. High-pass unnecessary low-end rumble.
Translation: Well-managed low-end on analyzer translates to tight, punchy bass on all playback systems.
6. Harshness & Sibilance Detection
Problem Frequencies: Use analyzer to identify harsh peaks in 2-8 kHz range that cause listener fatigue.
Vocal Sibilance: Insert on vocal channel, watch for excessive energy at 5-8 kHz during "S" sounds.
Treatment: Use de-esser targeting the specific frequency shown on analyzer, or manual EQ cut with narrow Q.
Verification: Re-analyze after processing to confirm harsh frequencies are tamed without losing presence.